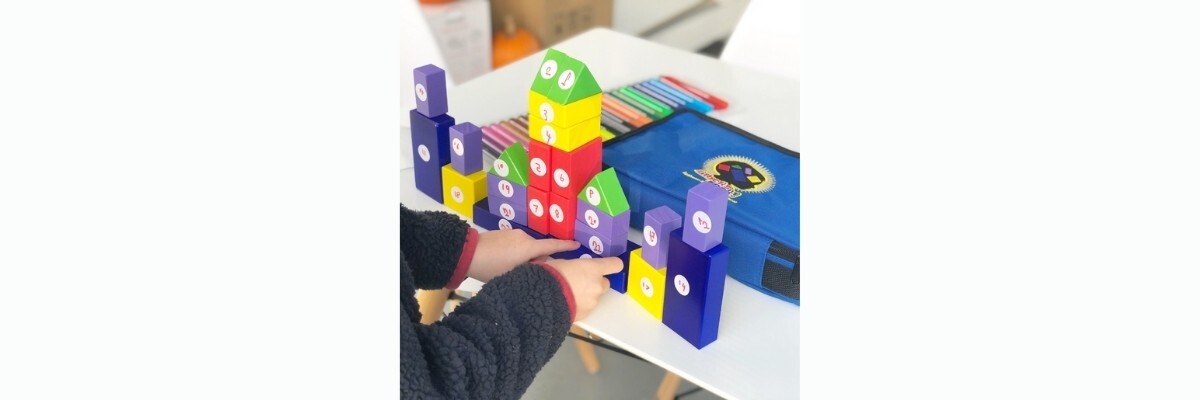
Block play has long been a favorite learning center in preschool classrooms and child care centers, but it can also be used in both preschool and elementary classrooms to promote STEM. A major benefit of using block play to promote science, technology, engineering, and mathematics is the versatile learning opportunities block play presents. Children can learn a variety of skills and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the concepts they are learning in class by playing with blocks. In regards to STEM, block play helps children nurture and develop skills in each discipline:
Science
Sharon MacDonald explains in Block Play: The Complete Guide to Learning and Playing with Blocks that children can explore cause and effect and learn about gravity, stability, weight, and balance as they play with blocks in the classroom. Inductive thinking, experimentation, properties of matter, and inclined planes can be incorporated into block play in elementary school.
The anterior approach to a sciatic block is an advanced nerve block technique. The block is suited for surgery on the leg below the knee, particularly on the ankle and foot. It provides complete anesthesia of the leg below the knee with the exception of the medial strip of skin innervated by the saphenous nerve ( Figure 19 ). Programmatic Modeling Basics. You can perform most Simulink ® modeling basics programmatically at the MATLAB ® Command Window, such as creating models, adding blocks to models, and setting parameters. These examples show some of these commands and how you can use them. Loading a model brings it into memory but does not open it in the Simulink Editor for editing.


Technology
Block play can help children develop the fine and gross motor skills they need to use technological devices. Having a classroom camera that children can use to take pictures of their designs and structures can also help children learn technology skills.
Engineering
You can use blocks or other building items, such as Magna-Tiles®, to help children learn about engineering concepts and develop problem-solving skills. Children can learn about architecture and the names and functions of different buildings and bridges as they build their own unique structures. They can also experiment with different designs and learn why some designs work and others fall down.
Mathematics
Block play helps children learn to express quantities and measurements, sort and match objects based on similarities and differences, and understand basic math concepts (numbers, shapes, counting, addition, subtraction, etc.). You can also use block play to help older children learn about fractions, symmetry, graphing, classification, and other mathematical concepts.
If you follow the STEAM philosophy, designing and building block structures also provides various art opportunities for children by encouraging them to think creatively. You can also have children paint and decorate homemade block items as a related activity.
Keep in mind that block play can help children nurture and develop a variety of other skills that are important to their overall development and success. Social-emotional skills (working with others, taking initiative, respecting others, etc.), language and literacy skills (learning new vocabulary words, exchanging ideas, naming buildings, etc.), and social studies skills (learning about the community, understanding people and their work, role playing, etc.) are just a few examples of the additional learning opportunities block play provides children.
Check out Block Play: The Complete Guide to Learning and Playing with Blocks for a variety of block play activities. Our block play section will also help you find blocks and other building materials that you can incorporate into your preschool and elementary classroom.
Additional Resources
Blocks vs. Manipulatives: Is There A Difference?
How to Set Up Your Preschool Block Learning Center
Recommended Products
Approaching Blocks For A
Unit Blocks - Basic Classroom SetsApproaching Black - Alone Again

Approaching Black
Brick, Blocks, and Rock BuildersApproaching Black Music
